What Is an SEO Strategy?
An SEO strategy is a long-term plan outlining how you’ll improve your website’s visibility in unpaid search engine results (also known as organic search results).
An SEO strategy typically covers the three core aspects of search engine optimization, which are on-page SEO, off-page SEO, and technical SEO.
- On-page SEO: Improving the relevance and quality of specific webpages
- Off-page SEO: Getting other people to talk about your brand and link to your website
- Technical SEO: Making your website perform better for users and search engines
Why Is Having an SEO Strategy Important?
Having an SEO strategy is important for growing visibility in search engines because it helps you make smarter decisions, keep your team aligned, and use resources more effectively.
A strong SEO strategy increases your chances of earning impressions, attracting traffic, and driving conversions at a relatively low cost.
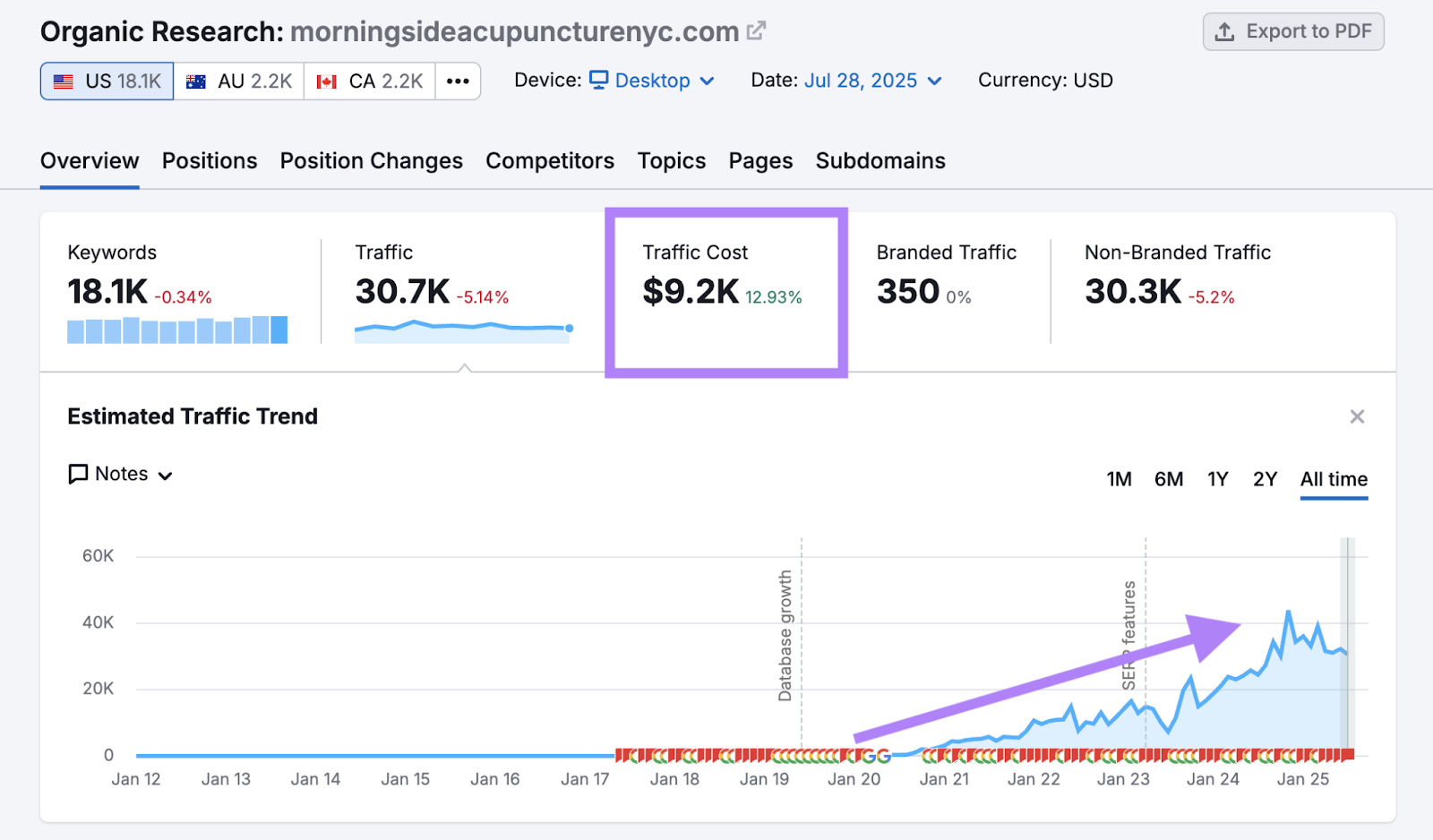
For example, Morningside Acupuncture NYC started investing in SEO in 2020. Within two years, the company quadrupled its revenue as a result of increased organic search traffic.
And the business has continued to grow since. In July 2025, the website earned organic search traffic worth $9.2K in advertising costs, according to Semrush’s Organic Research tool.
Here’s how to create an SEO strategy, step by step:
Step 1. Perform Keyword Research
The first step to creating an SEO strategy is performing SEO keyword research, which means identifying queries you want to show for in organic search results.
Basically, you’re looking for keywords that target audiences use during relevant buying journeys that involve search engines.
Here’s an example of a buyer’s journey through search:

Keywords give you insight into users’ needs. And using keywords effectively can help you rank higher in search results because they help search engines understand your content’s relevance.
So, keyword research is crucial to focusing your SEO efforts in the right areas.
You can perform basic keyword research by typing relevant terms into Google and seeing what autocomplete suggestions show up.
Or by looking at related searches, People Also Ask, and other search suggestions on the search engine results page (SERP).

To perform more advanced keyword research, use a free or paid keyword research tool.
Tools can help you find keywords you might have otherwise missed. And tools typically provide useful keyword metrics to help you prioritize your SEO efforts.
For example, Semrush’s Keyword Magic Tool lets you efficiently search Semrush’s database of over 27.2 billion keywords and access metrics including:
- Volume: The average number of monthly searches for a keyword. This gives you an indication of your search result’s potential reach.
- Keyword difficulty: How hard it’ll be to earn a high ranking for a keyword. This is important because higher-ranking results typically get more impressions and clicks.
- Intent: The general purpose behind the user’s search, which can be informational, navigational, commercial, or transactional. This helps you understand what the user is looking for and how likely they are to convert.
All you have to do is enter a term to base your search around along with your target country.
Then, use the filters, sorting options, and metrics to find the best keyword results.

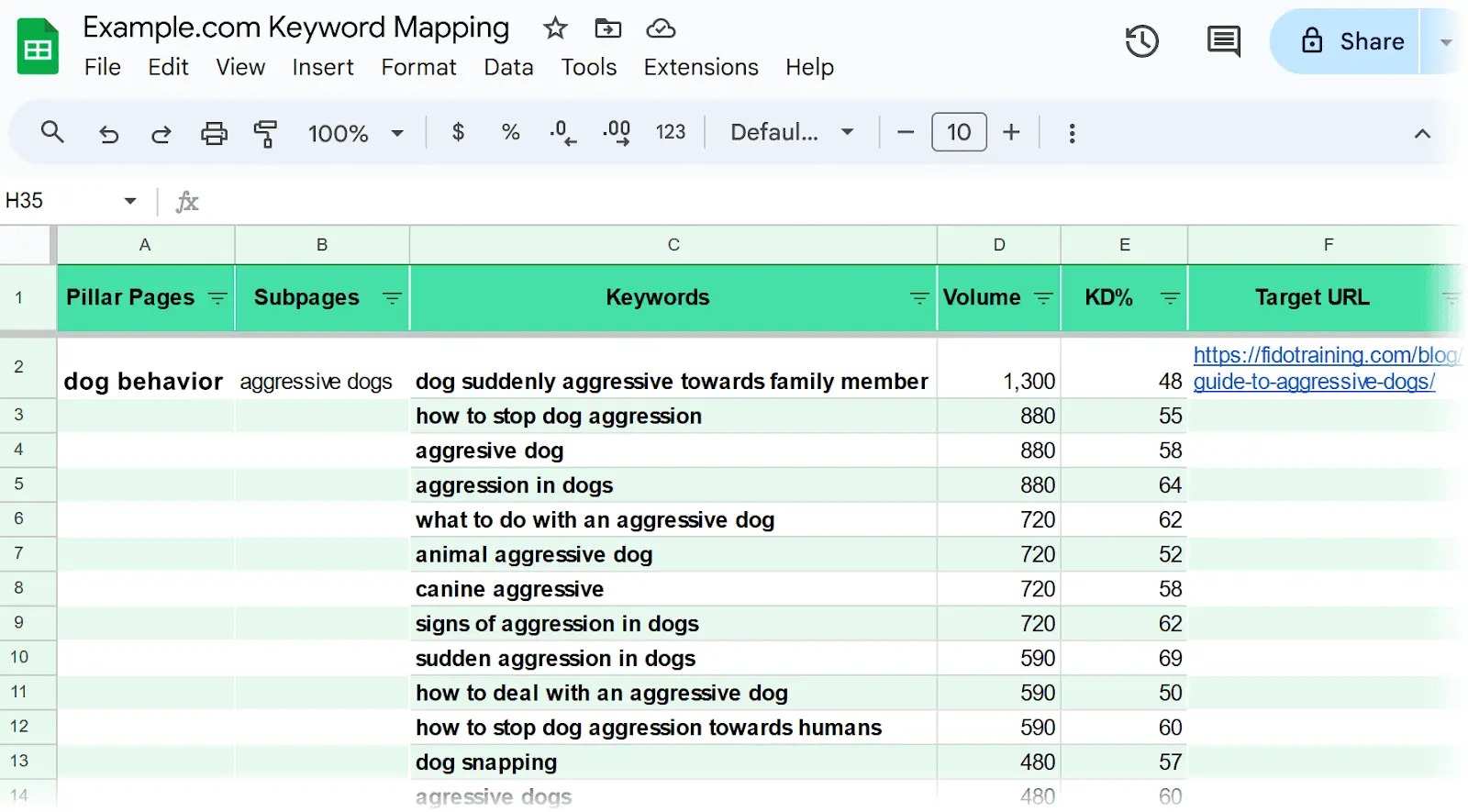
Step 2. Make a Keyword Map
A keyword map is a document matching each target keyword with the webpage on your site that has the potential to satisfy search intent (what the user wants).
If you don’t already have a page that satisfies search intent, you can plan to create one as part of your SEO strategy.
Keyword mapping is helpful because it helps you group together keywords that share intent so you can target your keywords in the right places.
You can also group together related pages and turn them into topic clusters (each with a main pillar page and multiple subpages). The idea is to link these pages together when you publish them to help users and search engines understand their relation.
Here’s a snapshot of an example keyword map:
To get insight into search intent for a keyword, check what websites, pages, formats, topics, and angles perform well on the SERP.
For example, the SERP below is dominated by listicles on editorial websites. Other types of websites and pages may struggle to compete for this keyword.
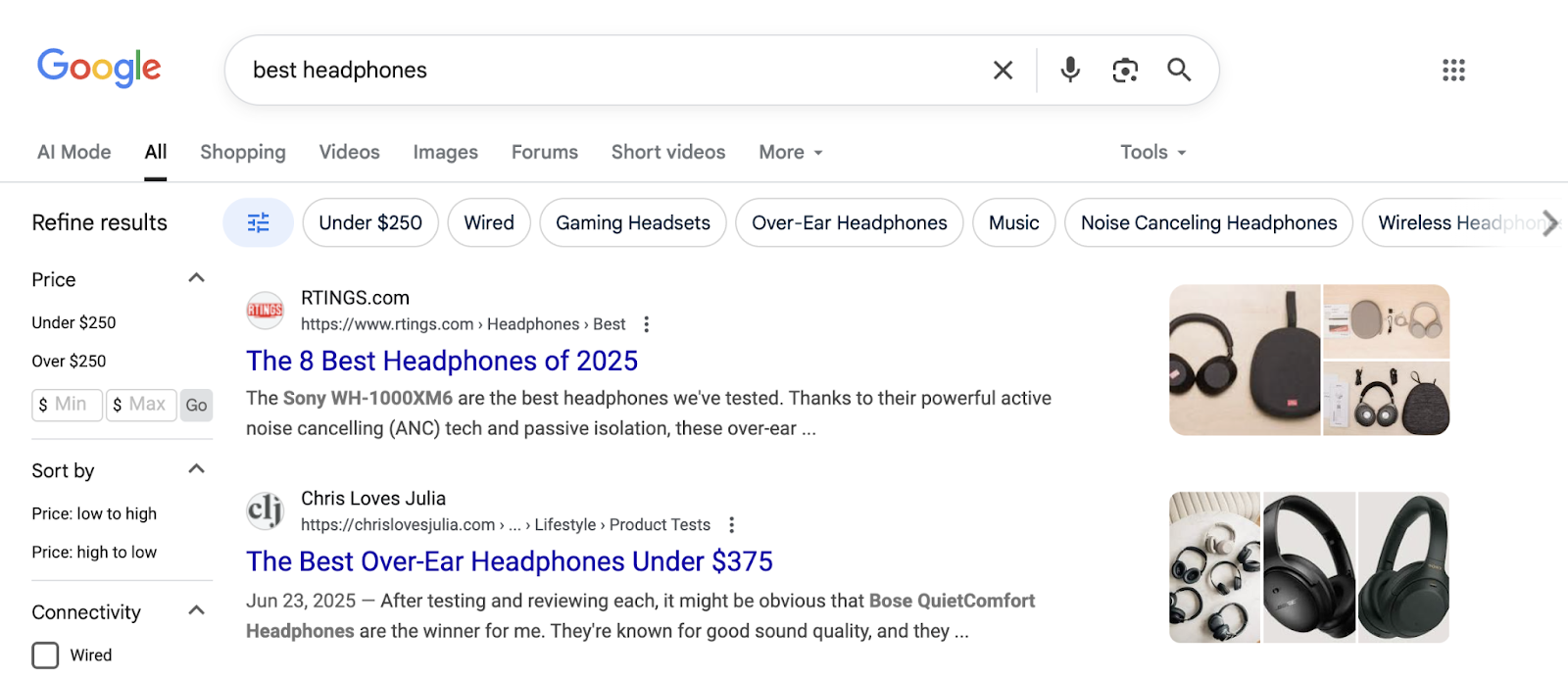
Do this for all your terms and group them accordingly.
Step 3. Create a Content Plan
A content plan is a document detailing what content you’re going to improve or create.
Content planning is a vital part of your SEO strategy because search engines prioritize helpful content that satisfies search intent clearly and comprehensively. And there are many ways to make your content more search engine-friendly.
Go through the already-published pages listed in your keyword map and consider the following questions:
- Does your content satisfy search intent comprehensively?
- Is your content accurate and up to date?
- Does your page offer anything valuable that competing pages don’t?
- Is your content easy to read, well formatted, and well structured?
- Does your page use videos, images, or other elements to support users’ understanding?
- Does your page have a descriptive title tag (HTML title) and H1 tag (on-page title)?
- Have you naturally incorporated relevant keywords into your content?
If the answer to any of these questions is no, you have an opportunity to improve your content.
You may wish to prioritize projects based on the content’s current quality level, the commercial importance of the page, and the potential value of the page. (This is where search volumes and keyword difficulty scores can come in handy.)
For help prioritizing, use Semrush’s On Page SEO Checker. The tool provides a variety of tailored optimization ideas based on the top-ranking results for your target keywords. And prioritizes pages based on their level of untapped potential.
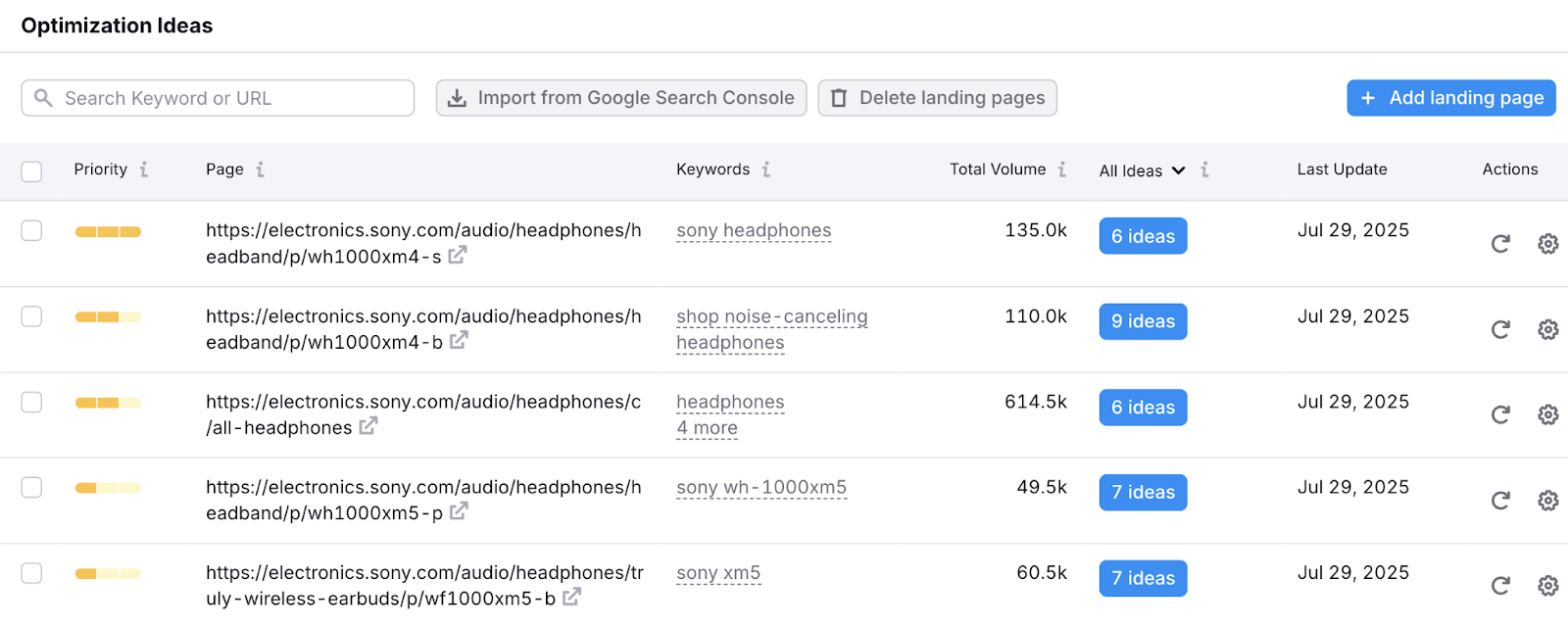
Once you’ve improved existing content, you can look to create new content that meets quality guidelines.
Step 4. Fix Technical SEO Issues
Fixing technical SEO issues can boost your website’s visibility in search engines, so you should identify these issues while building your SEO strategy.
You can check for many technical SEO issues through Google Search Console (a free tool from Google).
After setting up the tool, look through these reports:
- Page indexing: Shows which pages aren’t included in Google’s index (database of possible search results) and explains why. If you have pages that aren’t indexed but should be, take corrective action as soon as possible.
- Video indexing: Shows which pages contain a video that Google hasn’t indexed and explains why. If you take corrective action, Google may display your videos directly in search results.
- Sitemaps: Shows XML sitemaps you’ve submitted to Google. Submitting an up-to-date sitemap can help Google crawl and index your site efficiently.
- Core Web Vitals: Shows how your webpages perform for three page experience metrics known collectively as Core Web Vitals. Improving these metrics and getting more “Good” URLs could help you rank higher in Google’s search results.
- HTTPS: Shows whether you have any non-HTTPS URLs on your website. Google recommends using HTTPS encryption across your website to improve security.
- Manual actions: Shows whether you have any manual actions (also known as Google penalties) against your website. This means a human reviewer has flagged your site for violating Google policies, and it can seriously harm your search visibility. You should take corrective action as soon as possible.
- Security issues: Shows whether Google has flagged hacked content, malware, or social engineering on your website. You should fix these issues and request a reconsideration review as soon as possible.
Check for additional SEO issues and get help prioritizing them with Semrush’s Site Audit tool.
The tool categorizes issues into “Errors” (high priority), “Warnings” (medium priority), and “Notices” (low priority). And provides advice on how and why to fix each issue.
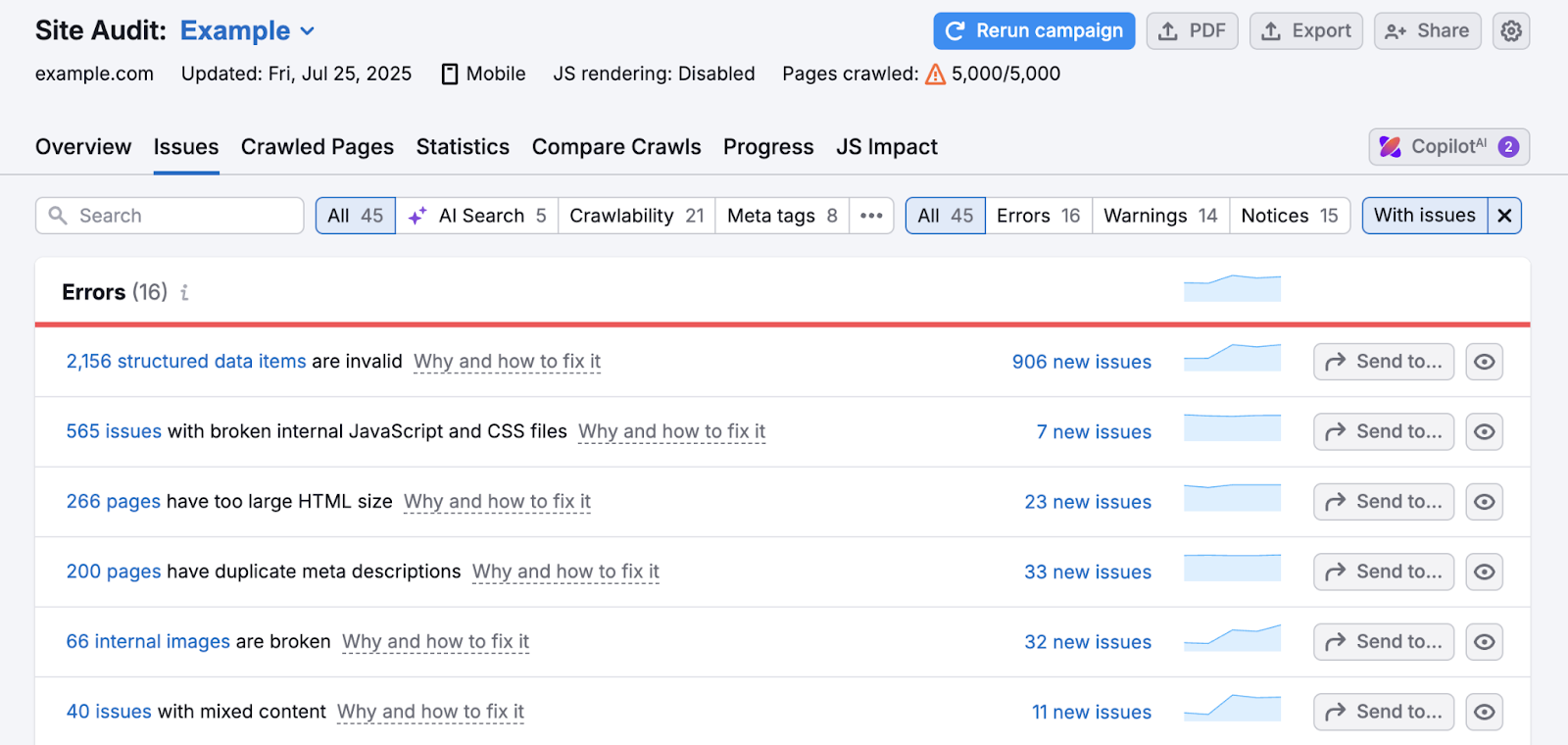
Some examples of common technical SEO errors include:
- Duplicate content: Pages with at least 85% identical content may be considered duplicates and harm your visibility in search results
- Broken internal links: Links between pages on your site that don’t work properly, which cause issues for users and search engine crawlers
- Robots.txt formatting errors: Errors in the robots.txt file, which is supposed to instruct search engines on which pages to crawl and which pages to avoid
- Redirect chains: Instances where a page redirects to a page that redirects elsewhere, which create unnecessary work for search engine crawlers
- Invalid structured data: Incorrectly formatted schema markup, which can prevent search engines from understanding and displaying your content correctly
Step 5. Plan How to Get Backlinks and Mentions
Backlinks (links to your website from other websites) and mentions (references to your brand on other websites) can make your brand appear more prominent, trustworthy, and authoritative to search engines. And contribute to higher search visibility.
So, plan how to get backlinks and mentions as part of your SEO strategy.
First, identify tactics that are most likely to work for your brand. The best options depend on your niche and available resources.
Here are some of the tactics to consider:
- Digital PR: Generate and distribute newsworthy content
- Broken link building: Identify broken links pointing to your own or competitors’ websites and try to get them replaced with working links to your website
- Guest posting: Write high-quality articles for relevant and reputable websites
- Link baiting: Create high-quality content that naturally attracts links (e.g., original studies)
- Become a source: Respond to media requests for commentary, images, etc.
Next, identify prospects (websites you want to get links or mentions from).
Your prospects should be relevant and reputable sites that publish high-quality content. Backlinks and mentions from these sites are most likely to enhance your reputation and benefit your search visibility.
You can find prospects by searching Google for relevant terms or using a specialist tool.
For example, Semrush’s Link Building Tool identifies link building prospects based on your target keywords and competitors.
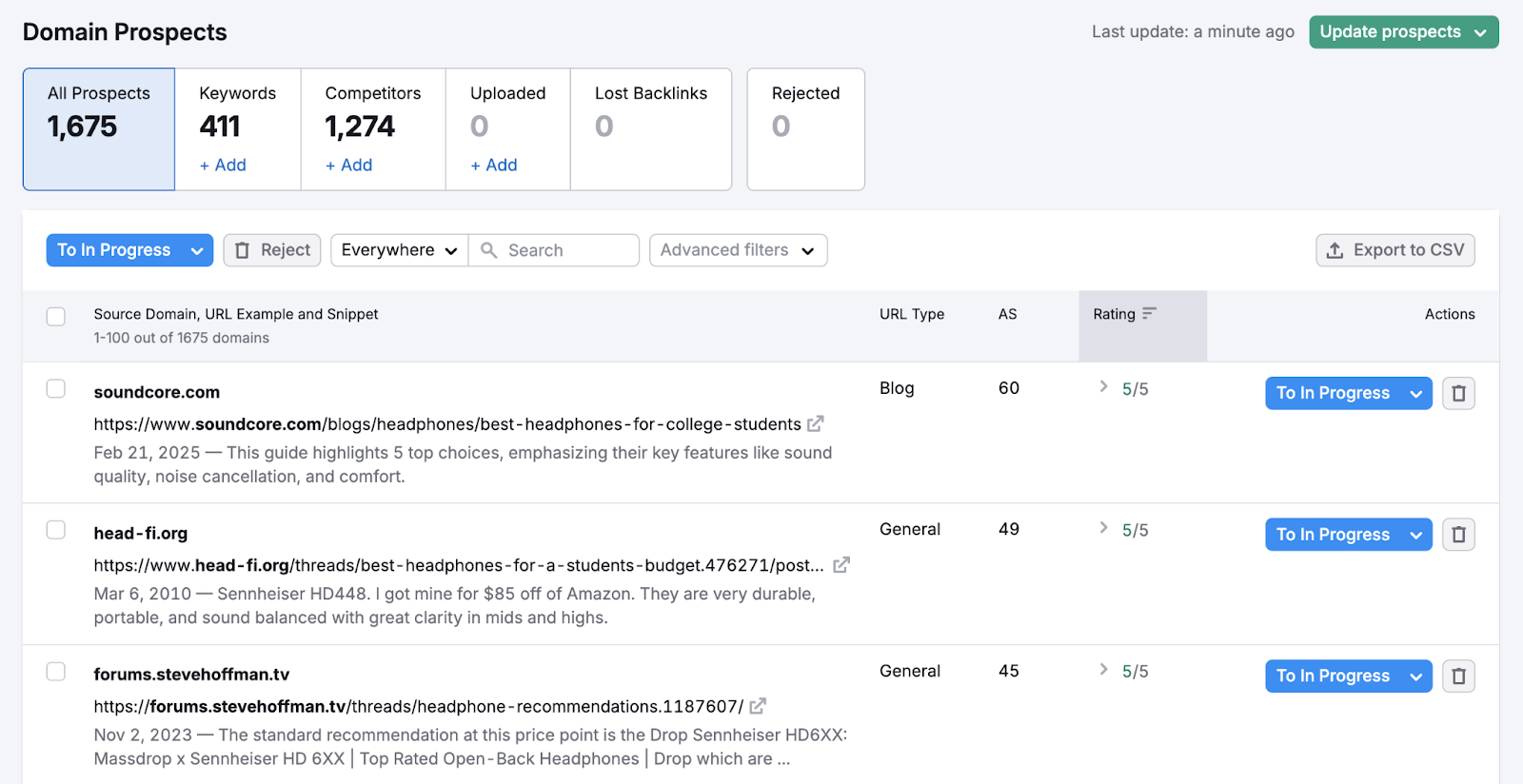
The tool can also help you to start and track conversations with your chosen prospects.
Step 6. Decide How to Track Your SEO Results
Tracking your SEO results lets you see what’s working and what isn’t, so you can refine your SEO strategy over time.
Start by deciding what metrics you need to track and how you’re going to track them.
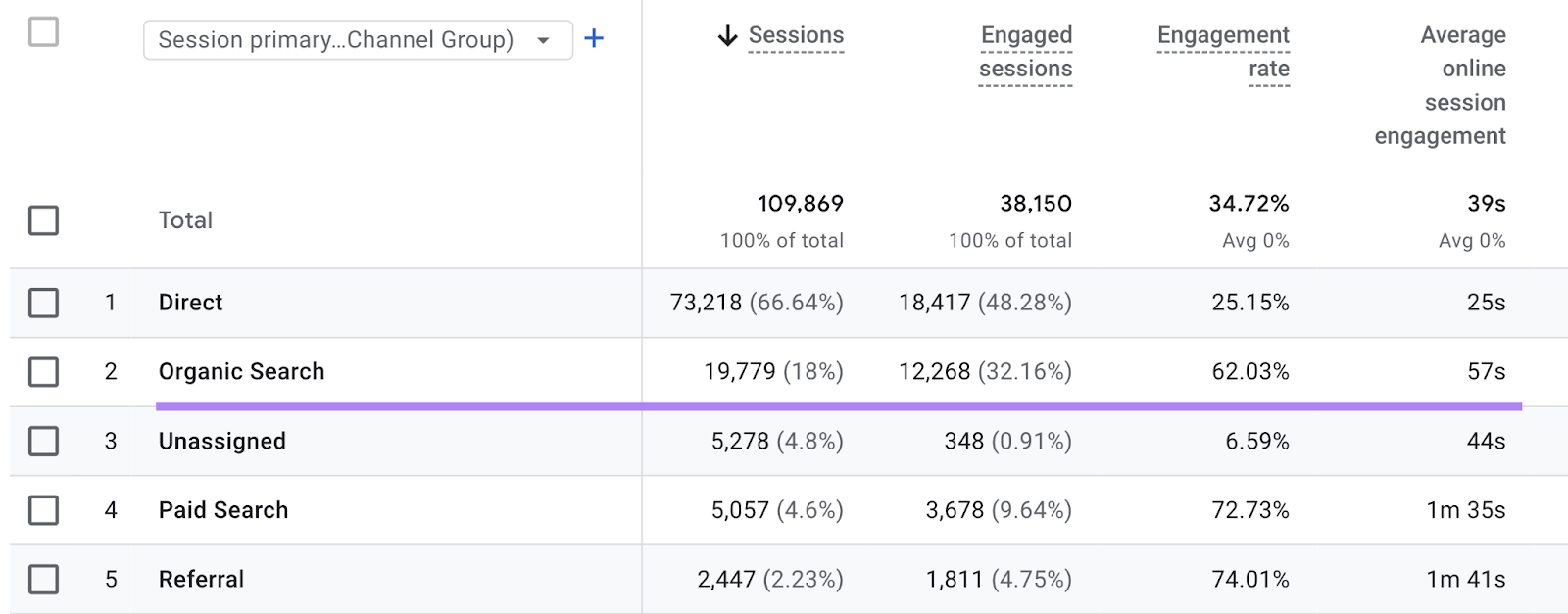
If you haven’t already, sign up for Google Analytics 4. This is a free website analytics platform that lets you review metrics on a site-wide or page-by-page basis.
You can measure organic search metrics, including:
- Sessions: How many visits originate from organic search results
- Average online session engagement: How long the average session lasts
- Conversion events: How many desired events (e.g., purchases) originate from organic search sessions
For insight into SERP position fluctuations, track your keyword rankings.
You can see your organic rankings for up to 1,000 top queries chosen by Google in Google Search Console. Just head to “Performance” > “Search results.”
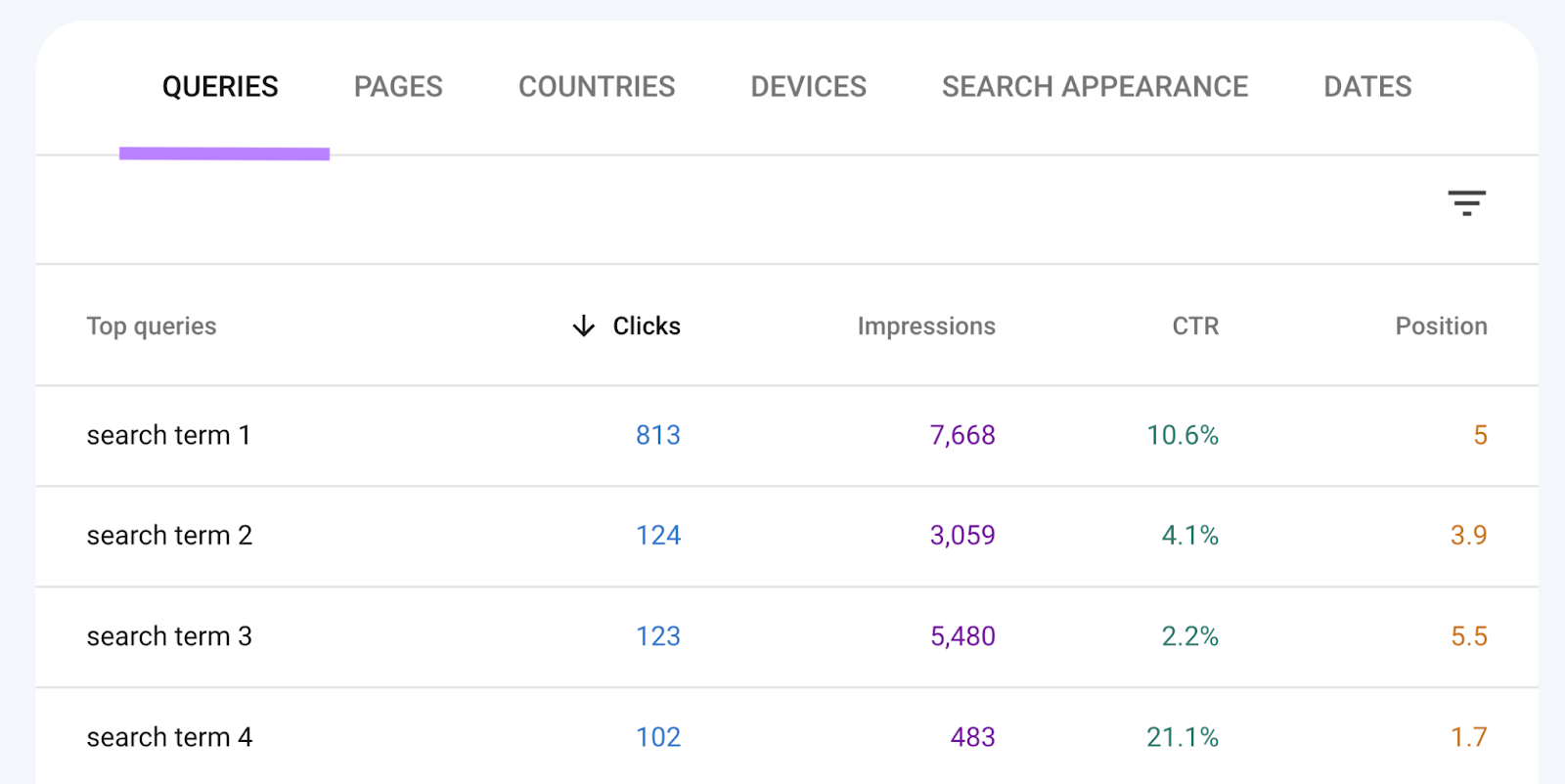
Alternatively, track your chosen keywords in Semrush’s Position Tracking tool.
In addition to showing your organic rankings, the tool displays keyword metrics, lets you compare your rankings against competitors’, and shows whether your website appears in SERP features such as AI Overviews.

Step 7. Start Optimizing for LLMs
Enhance and future-proof your SEO strategy by optimizing for large language models (LLMs). This can help your brand show in AI search responses, like those on ChatGPT and Google AI Mode.
Here’s an example of a ChatGPT response that could benefit the featured brands and websites:
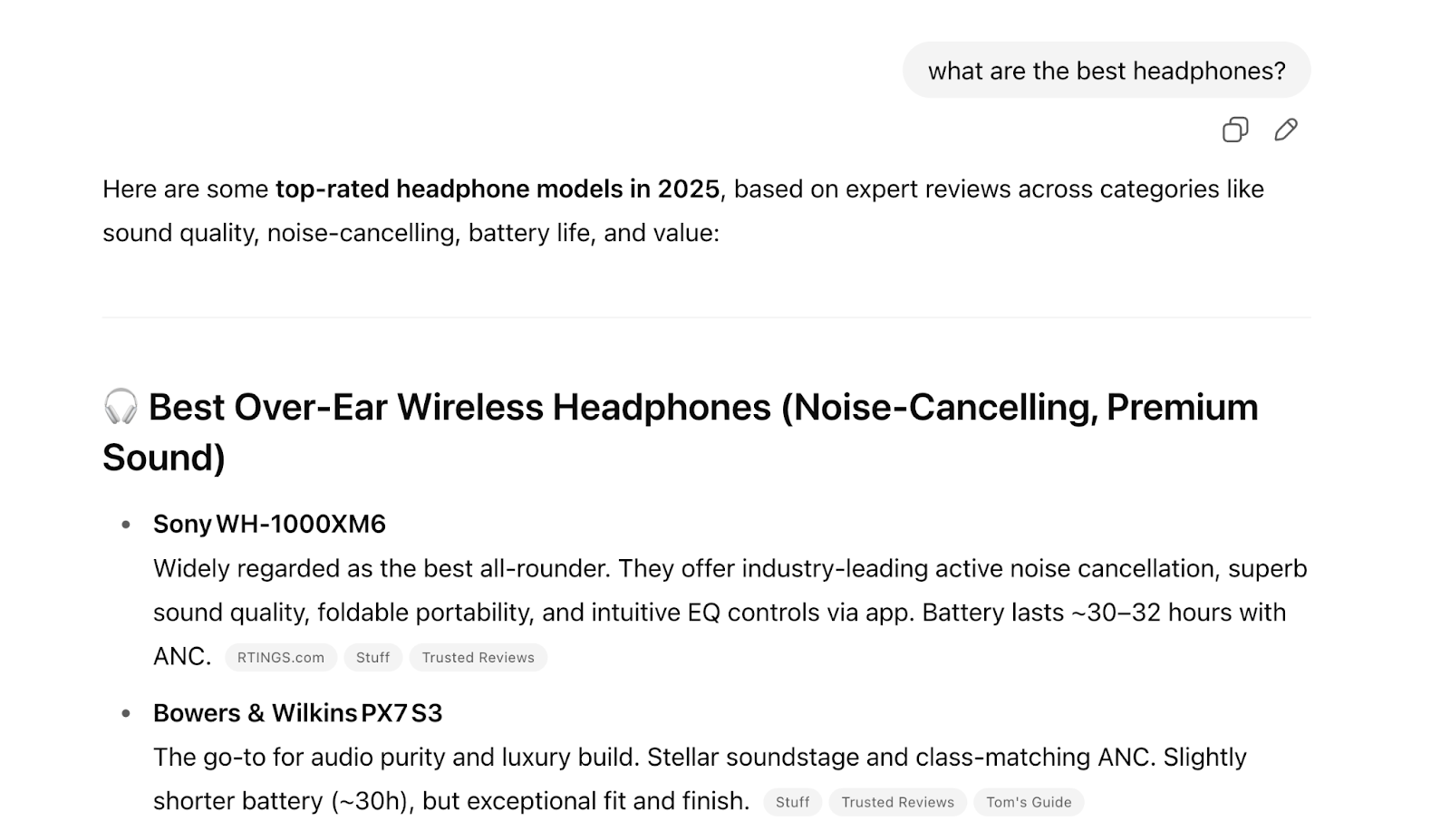
Semrush research shows that AI search visitors are 4.4x more valuable than traditional search visitors. And that AI search traffic could exceed traditional search traffic by 2028.
By acting now, you could generate immediate results for your business. And build a strong foundation for an AI-dominant future.
Here are our top tips for LLM optimization:
- Build a unique value proposition (UVP) and communicate it consistently
- Tailor your content to a clearly defined target audience
- Get your brand featured positively on commonly cited websites (websites that LLMs regularly use as information sources in your niche)
- Manage and protect your online reputation
- Encourage customers to leave online reviews
- Make sure your content is accessible to LLM crawlers, where appropriate
- Avoid unclear language and complex sentence structures
Many LLM optimization tactics can assist your SEO performance—and vice versa. So, your efforts can have a doubly positive impact.
Build and Execute Your SEO Strategy
The Semrush SEO Toolkit provides a variety of tools to help you build and execute a successful SEO strategy, including:
- Keyword Magic Tool: Discover and analyze search terms your audience uses in Google
- On Page SEO Checker: Get tailored optimization ideas for your webpages
- Site Audit: Find technical SEO issues on your website and learn how to them
- Link Building Tool: Identify and contact solid link building prospects
- Position Tracking: Monitor your Google rankings for your chosen keywords
Sign up free to try them out.